spraseArray&ArrayMap源码分析
SparseArray
摘要:
内部是通过两个数组来进行数据存储的,一个是Int数组存储 key,避免了对 key 的自动装箱,另外一个是object数据存储 value
对数据还采取了压缩的方式,从而节约内存空间。
这一点体现在创建object数组时使用是使用ArrayUtils去创建一个稀疏数组,它解决了当数组中的元素没有填满时造成的空间浪费。
同时,SparseArray 在存储和读取数据时候,使用的是二分查找法。也就是说SparseArray 存储的元素都是按元素的 key 值从小到大排列好的,一般来说,SparseArray执行效率比HashMap要慢一点,我们使用它主要是为了降低内存占用
构造函数
首先看到构造函数
val sparseArray = SparseArray<Looper>()
/**
* Creates a new SparseArray containing no mappings.
*/
public SparseArray() {
this(10);
}
/**
* Creates a new SparseArray containing no mappings that will not
* require any additional memory allocation to store the specified
* number of mappings. If you supply an initial capacity of 0, the
* sparse array will be initialized with a light-weight representation
* not requiring any additional array allocations.
*/
public SparseArray(int initialCapacity) {
if (initialCapacity == 0) {
mKeys = EmptyArray.INT;
mValues = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else {
//使用ArrayUtils去创建一个稀疏数组,它解决了当数组中的元素没有填满时造成的空间浪费。
mValues = ArrayUtils.newUnpaddedObjectArray(initialCapacity);
//key为int数组
mKeys = new int[mValues.length];
}
mSize = 0;
}
这里重点关注俩点
1.内部是通过两个数组来进行数据存储的,一个是Int数组存储 key,避免了对 key 的自动装箱,另外一个是object数据存储 value
2.创建object数组时使用是使用ArrayUtils去创建一个稀疏数组,它解决了当数组中的元素没有填满时造成的空间浪费。
稀疏数组得原理如下图:
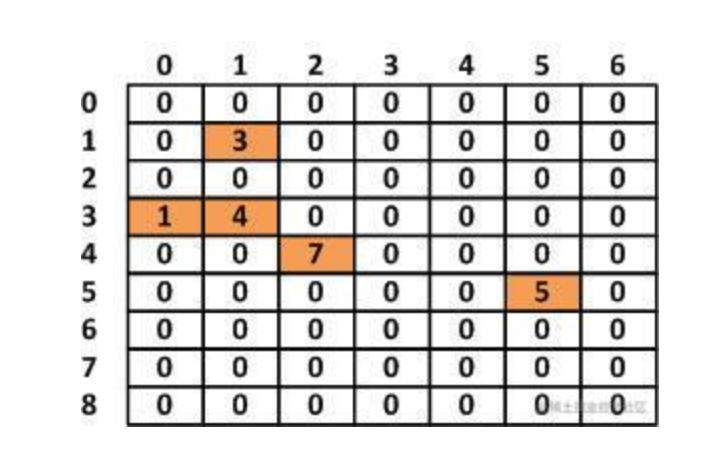
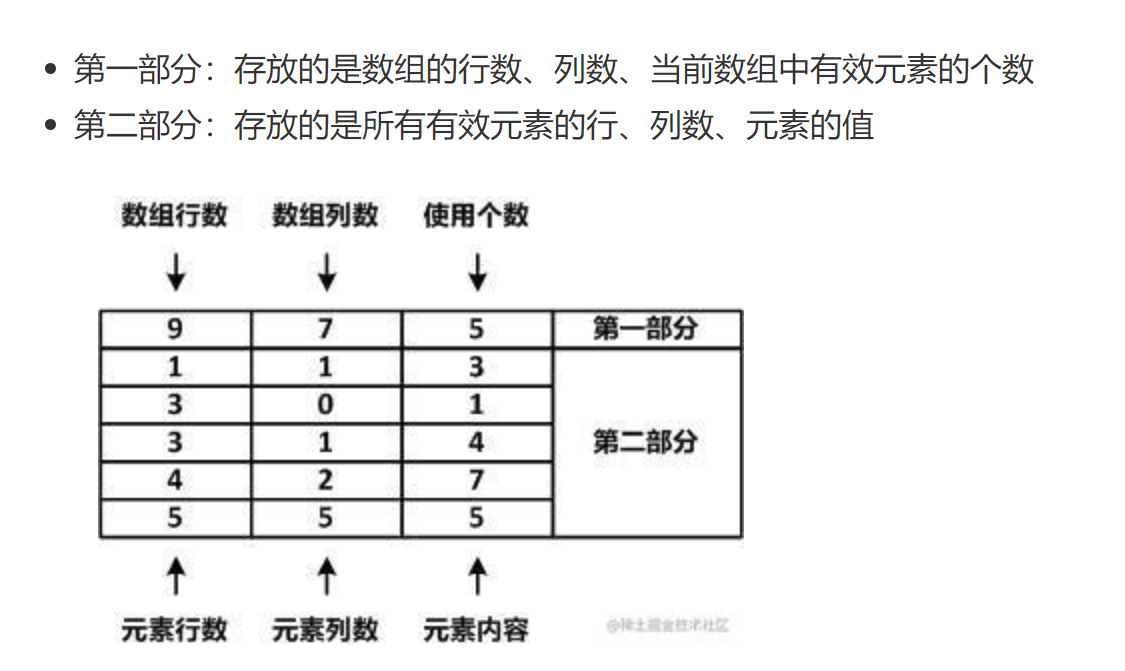
存数据
/**
* Adds a mapping from the specified key to the specified value,
* replacing the previous mapping from the specified key if there
* was one.
*/
public void put(int key, E value) {
//通过二分查找法进行查找插入元素所在位置,如果二分查找没有找到值那么会将lo取反返回
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i >= 0) {
mValues[i] = value;
} else {
i = ~i;
//如果插入的位置之前已经分配,但是该位置上的元素已经被标记为删除,那么直接替换
if (i < mSize && mValues[i] == DELETED) {
mKeys[i] = key;
mValues[i] = value;
return;
}
if (mGarbage && mSize >= mKeys.length) {
//回收掉已经标记为deleted的元素
gc();
// Search again because indices may have changed.
i = ~ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
}
//往数组指定位置插入数据
mKeys = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mKeys, mSize, i, key);
mValues = GrowingArrayUtils.insert(mValues, mSize, i, value);
mSize++;
}
}
//ContainerHelpers#binarySearch
// This is Arrays.binarySearch(), but doesn't do any argument validation.
static int binarySearch(int[] array, int size, int value) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = size - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
final int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
final int midVal = array[mid];
if (midVal < value) {
lo = mid + 1;
} else if (midVal > value) {
hi = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid; // value found
}
}
return ~lo; // value not present
}
//gc()
private void gc() {
int n = mSize;
int o = 0;
int[] keys = mKeys;
Object[] values = mValues;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i++) {
Object val = values[i];
if (val != DELETED) {
if (i != o) {
keys[o] = keys[i];
values[o] = val;
values[i] = null;
}
o++;
}
}
mGarbage = false;
mSize = o;
}
//GrowingArrayUtils#insert
public static <T> T[] insert(T[] array, int currentSize, int index, T element) {
if (currentSize + 1 <= array.length) {
System.arraycopy(array, index, array, index + 1, currentSize - index);
array[index] = element;
return array;
}
T[] newArray = (T[]) Array.newInstance(array.getClass().getComponentType(),
growSize(currentSize));
System.arraycopy(array, 0, newArray, 0, index);
newArray[index] = element;
System.arraycopy(array, index, newArray, index + 1, array.length - index);
return newArray;
}
取数据
取数据就比较简单了
/**
* Gets the Object mapped from the specified key, or <code>null</code>
* if no such mapping has been made.
*/
public E get(int key) {
return get(key, null);
}
/**
* Gets the Object mapped from the specified key, or the specified Object
* if no such mapping has been made.
*/
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public E get(int key, E valueIfKeyNotFound) {
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i < 0 || mValues[i] == DELETED) {
return valueIfKeyNotFound;
} else {
return (E) mValues[i];
}
}
通过key二分查找数据,没找到就返回null或者一个自己定义的默认值
删除数据
可以看到,在删除元素的时候,它是用一个空的Object来标记该位置。在合适的时候(例如上面的put方法),才通过gc()对mKeys和mValues数组 重新排列。
/**
* Removes the mapping from the specified key, if there was any.
*/
public void delete(int key) {
int i = ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(mKeys, mSize, key);
if (i >= 0) {
if (mValues[i] != DELETED) {
mValues[i] = DELETED;
mGarbage = true;
}
}
}
ArrayMap
摘要:
ArrayMap 利用两个数组,一个数组用来保存每一个 key 的 hash 值,第二个数组大小为 第一个数组大小 的 2 倍,依次保存 key 和 value。
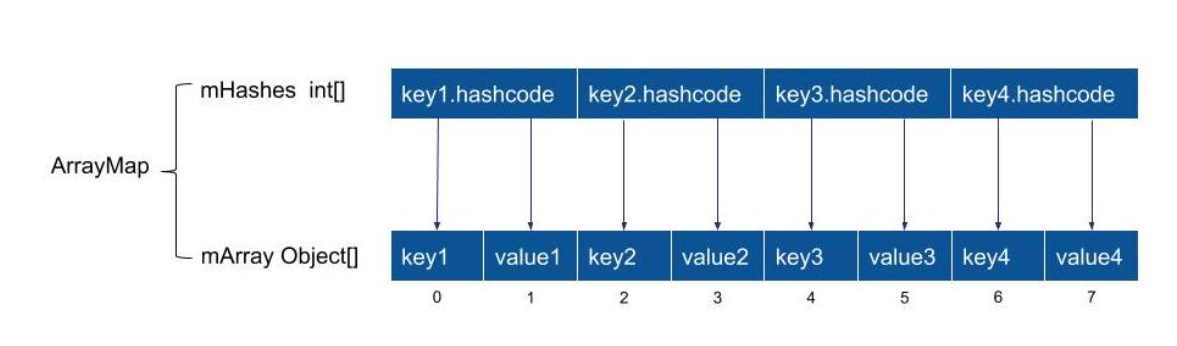
当插入时,根据 key 的 hashcode得到 hash 值,计算出在 mArrays 的 index位置,然后利用二分查找找到对应的位置进行插入,当出现哈希冲突时,会在index 的相邻位置插入。
构造函数
/**
* Create a new empty ArrayMap. The default capacity of an array map is 0, and
* will grow once items are added to it.
*/
public ArrayMap() {
this(0, false);
}
/**
* Create a new ArrayMap with a given initial capacity.
*/
public ArrayMap(int capacity) {
this(capacity, false);
}
/** {@hide} */
public ArrayMap(int capacity, boolean identityHashCode) {
mIdentityHashCode = identityHashCode;
// If this is immutable, use the sentinal EMPTY_IMMUTABLE_INTS
// instance instead of the usual EmptyArray.INT. The reference
// is checked later to see if the array is allowed to grow.
if (capacity < 0) {
mHashes = EMPTY_IMMUTABLE_INTS;
mArray = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else if (capacity == 0) {
mHashes = EmptyArray.INT;
mArray = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
} else {
//这个在缓存机制中进行了分析
allocArrays(capacity);
}
mSize = 0;
}
缓存机制
ArrayMap是专为Android优化而设计的Map对象,使用场景比较高频,为了减少频繁地创建和回收,特意设计了两个缓存池mBaseCache和mTwiceBaseCacheSize,用于ArrayMap所在进程的全局缓存功能,分别缓存大小为4和8的ArrayMap对象,并且都超过10个则不再缓存。要理解缓存机制,那就需要看看内存分配(allocArrays)和内存释放(freeArrays)。
数据结构:
public final class ArrayMap<K, V> implements Map<K, V> {
private static final int BASE_SIZE = 4; // 容量增量的最小值
private static final int CACHE_SIZE = 10; // 缓存数组的上限
/**
* Caches of small array objects to avoid spamming garbage. The cache
* Object[] variable is a pointer to a linked list of array objects.
* The first entry in the array is a pointer to the next array in the
* list; the second entry is a pointer to the int[] hash code array for it.
*/
static Object[] mBaseCache; //用于缓存大小为4的ArrayMap
static int mBaseCacheSize;
static Object[] mTwiceBaseCache; //用于缓存大小为8的ArrayMap
static int mTwiceBaseCacheSize;
/**
* Separate locks for each cache since each can be accessed independently of the other without
* risk of a deadlock.
*/
private static final Object sBaseCacheLock = new Object();
private static final Object sTwiceBaseCacheLock = new Object();
int[] mHashes; //由key的hashcode所组成的数组
Object[] mArray; //由key-value对所组成的数组,是mHashes大小的2倍
int mSize; //成员变量的个数
}
freeArrays
/**
* Make sure NOT to call this method with arrays that can still be modified. In other
* words, don't pass mHashes or mArray in directly.
*/
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = 28) // Allocations are an implementation detail.
private static void freeArrays(final int[] hashes, final Object[] array, final int size) {
if (hashes.length == (BASE_SIZE * 2)) {//当释放的是大小为8的对象
synchronized (sTwiceBaseCacheLock) {
// 当大小为8的缓存池的数量小于10个,则将其放入缓存池
if (mTwiceBaseCacheSize < CACHE_SIZE) {
array[0] = mTwiceBaseCache; //array[0]指向原来的缓存池
array[1] = hashes;
for (int i = (size << 1) - 1; i >= 2; i--) {
array[i] = null; //清空其他数据
}
mTwiceBaseCache = array; //mTwiceBaseCache指向新加入缓存池的array,这里的操作其实就是将mTwiceBaseCache作为了缓存数组链表的头指针
mTwiceBaseCacheSize++;
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "Storing 2x cache " + array
+ " now have " + mTwiceBaseCacheSize + " entries");
}
}
} else if (hashes.length == BASE_SIZE) { //当释放的是大小为4的对象,原理同上
synchronized (sBaseCacheLock) {
if (mBaseCacheSize < CACHE_SIZE) {
array[0] = mBaseCache;
array[1] = hashes;
for (int i = (size << 1) - 1; i >= 2; i--) {
array[i] = null;
}
mBaseCache = array;
mBaseCacheSize++;
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "Storing 1x cache " + array
+ " now have " + mBaseCacheSize + " entries");
}
}
}
}
当释放的数组对象大小为8或4时,并且缓存池的实时容量小于10时才会将其进行缓存
mTwiceBaseCache是一个数组对象链表的头节点,每次缓存时将新的缓存数组节点插入到链表头部
freeArrays()触发时机:
- 当执行removeAt()移除最后一个元素的情况
- 当执行clear()清理的情况
- 当执行ensureCapacity()在当前容量小于预期容量的情况下, 先执行allocArrays,再执行freeArrays
- 当执行put()在容量满的情况下, 先执行allocArrays, 再执行freeArrays
allocArrays
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = 28) // Allocations are an implementation detail.
private void allocArrays(final int size) {
if (mHashes == EMPTY_IMMUTABLE_INTS) {
throw new UnsupportedOperationException("ArrayMap is immutable");
}
if (size == (BASE_SIZE * 2)) { //当分配大小为8的对象,先查看缓存池
synchronized (sTwiceBaseCacheLock) {
if (mTwiceBaseCache != null) { // 当缓存池不为空时
final Object[] array = mTwiceBaseCache;
mArray = array; //从缓存池中取出mArray
try {
mTwiceBaseCache = (Object[]) array[0]; //将缓存池指向下一条缓存地址
mHashes = (int[]) array[1]; //从缓存中mHashes
if (mHashes != null) {
array[0] = array[1] = null;
mTwiceBaseCacheSize--; //缓存池大小减1
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "Retrieving 2x cache " + mHashes
+ " now have " + mTwiceBaseCacheSize + " entries");
}
return;
}
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
}
// Whoops! Someone trampled the array (probably due to not protecting
// their access with a lock). Our cache is corrupt; report and give up.
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Found corrupt ArrayMap cache: [0]=" + array[0]
+ " [1]=" + array[1]);
mTwiceBaseCache = null;
mTwiceBaseCacheSize = 0;
}
}
} else if (size == BASE_SIZE) { //当分配大小为4的对象,原理同上
synchronized (sBaseCacheLock) {
if (mBaseCache != null) {
final Object[] array = mBaseCache;
mArray = array;
try {
mBaseCache = (Object[]) array[0];
mHashes = (int[]) array[1];
if (mHashes != null) {
array[0] = array[1] = null;
mBaseCacheSize--;
if (DEBUG) {
Log.d(TAG, "Retrieving 1x cache " + mHashes
+ " now have " + mBaseCacheSize + " entries");
}
return;
}
} catch (ClassCastException e) {
}
// Whoops! Someone trampled the array (probably due to not protecting
// their access with a lock). Our cache is corrupt; report and give up.
Slog.wtf(TAG, "Found corrupt ArrayMap cache: [0]=" + array[0]
+ " [1]=" + array[1]);
mBaseCache = null;
mBaseCacheSize = 0;
}
}
}
// 分配大小除了4和8之外的情况,则直接创建新的数组
mHashes = new int[size];
mArray = new Object[size << 1];
}
当分配的数组对象大小为8或4时,并且缓存池中有缓存数据时才会从缓存池中取数据
allocArrays触发时机:
- 当执行ArrayMap的构造函数的情况
- 当执行removeAt()在满足容量收紧机制的情况
- 当执行ensureCapacity()在当前容量小于预期容量的情况下, 先执行allocArrays,再执行freeArrays
- 当执行put()在容量满的情况下, 先执行allocArrays, 再执行freeArrays
扩容和缩容
扩容:
//下面进行扩容操作
if (osize >= mHashes.length) {//当mSize大于或等于mHashes数组长度时,需要扩容
final int n = osize >= (BASE_SIZE * 2) ? (osize + (osize >> 1))
: (osize >= BASE_SIZE ? (BASE_SIZE * 2) : BASE_SIZE);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: grow from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
allocArrays(n); //分配更大的内存
//由于ArrayMap并非线程安全的类,不允许并行,如果扩容过程其他线程调整mSize则抛出异常
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS && osize != mSize) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
if (mHashes.length > 0) {
//将原来老的数组拷贝到新分配的数组
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: copy 0-" + osize + " to 0");
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, ohashes.length);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, oarray.length);
}
//释放原来老的内存
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, osize);
}
当mSize大于或等于mHashes数组长度时则扩容,完成扩容后需要将老的数组拷贝到新分配的数组,并释放老的内存。
- 当map个数满足条件 osize<4时,则扩容后的大小为4;
- 当map个数满足条件 4<= osize < 8时,则扩容后的大小为8;
- 当map个数满足条件 osize>=8时,则扩容后的大小为原来的1.5倍;
可见ArrayMap大小在不断增加的过程,size的取值一般情况依次会是4,8,12,18,27,40,60,…
缩容:
当remove元素时可能会发生缩容以节省内存
当数组内存的大小大于8,且已存储数据的个数mSize小于数组空间大小的1/3的情况下,需要收紧数据的内容容量,分配新的数组,老的内存靠虚拟机自动回收。
- 如果mSize<=8,则设置新大小为8;
- 如果mSize> 8,则设置新大小为mSize的1.5倍。
也就是说在数据较大的情况下,当内存使用量不足1/3的情况下,内存数组会收紧50%。
存元素
put
/**
* Add a new value to the array map.
*
* @param key The key under which to store the value. If
* this key already exists in the array, its value will be replaced.
* @param value The value to store for the given key.
* @return Returns the old value that was stored for the given key, or null if there
* was no such key.
*/
@Override
public V put(K key, V value) {
final int osize = mSize; //osize记录当前map大小
final int hash;
int index;
if (key == null) {
hash = 0;
index = indexOfNull();
} else {
//默认mIdentityHashCode=false,因此这里的hash是key的hashcode值
hash = mIdentityHashCode ? System.identityHashCode(key) : key.hashCode();
//采用二分查找法,从mHashes数组中查找
//查找规则见下面对indexOf方法的分析
index = indexOf(key, hash);
}
//当index大于零,则代表的是从数据mHashes中找到hashcode和key都相同的数据,执行的操作等价于修改mArray中的value
if (index >= 0) {
index = (index << 1) + 1;
final V old = (V) mArray[index];
mArray[index] = value;
return old;
}
//当index<0,则代表是插入新元素
index = ~index;
//下面进行扩容操作
if (osize >= mHashes.length) {
final int n = osize >= (BASE_SIZE * 2) ? (osize + (osize >> 1))
: (osize >= BASE_SIZE ? (BASE_SIZE * 2) : BASE_SIZE);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: grow from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
allocArrays(n);
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS && osize != mSize) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
if (mHashes.length > 0) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: copy 0-" + osize + " to 0");
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, ohashes.length);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, oarray.length);
}
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, osize);
}
//----扩容操作结束----
//当需要插入的位置不在数组末尾时,需要将index位置后的数据通过拷贝往后移动一位
if (index < osize) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "put: move " + index + "-" + (osize - index)
+ " to " + (index + 1));
System.arraycopy(mHashes, index, mHashes, index + 1, osize - index);
System.arraycopy(mArray, index << 1, mArray, (index + 1) << 1, (mSize - index) << 1);
}
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS) {
if (osize != mSize || index >= mHashes.length) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
}
//将hash、key、value添加相应数组的位置,数据个数mSize加1
mHashes[index] = hash;
mArray[index << 1] = key;
mArray[(index << 1) + 1] = value;
mSize++;
return null;
}
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = 28)
// Hashes are an implementation detail. Use indexOfKey(Object).
int indexOf(Object key, int hash) {
final int N = mSize;
// Important fast case: if nothing is in here, nothing to look for.
if (N == 0) {
return ~0;
}
//在mHashes数组中二分查找hash值,如果找到则index>0,没有找到则是将lo取反返回
int index = binarySearchHashes(mHashes, N, hash);
// If the hash code wasn't found, then we have no entry for this key.
if (index < 0) {
return index;
}
//因为有可能发生hash碰撞,所以还需要拿mArray存储的key来对比一下以确认是同一个
// If the key at the returned index matches, that's what we want.
if (key.equals(mArray[index << 1])) {
return index;
}
// Search for a matching key after the index.
int end;
for (end = index + 1; end < N && mHashes[end] == hash; end++) {
if (key.equals(mArray[end << 1])) return end;
}
// Search for a matching key before the index.
for (int i = index - 1; i >= 0 && mHashes[i] == hash; i--) {
if (key.equals(mArray[i << 1])) return i;
}
// Key not found -- return negative value indicating where a
// new entry for this key should go. We use the end of the
// hash chain to reduce the number of array entries that will
// need to be copied when inserting.
return ~end;
}
private static int binarySearchHashes(int[] hashes, int N, int hash) {
try {
return ContainerHelpers.binarySearch(hashes, N, hash);
} catch (ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException e) {
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
} else {
throw e; // the cache is poisoned at this point, there's not much we can do
}
}
}
class ContainerHelpers {
// This is Arrays.binarySearch(), but doesn't do any argument validation.
static int binarySearch(int[] array, int size, int value) {
int lo = 0;
int hi = size - 1;
while (lo <= hi) {
final int mid = (lo + hi) >>> 1;
final int midVal = array[mid];
if (midVal < value) {
lo = mid + 1;
} else if (midVal > value) {
hi = mid - 1;
} else {
return mid; // value found
}
}
return ~lo; // value not present
}
}
append
/**
* Special fast path for appending items to the end of the array without validation.
* The array must already be large enough to contain the item.
*
* @hide
*/
@UnsupportedAppUsage(maxTargetSdk = 28) // Storage is an implementation detail. Use put(K, V).
public void append(K key, V value) {
int index = mSize;
final int hash = key == null ? 0
: (mIdentityHashCode ? System.identityHashCode(key) : key.hashCode());
//使用append前必须保证mHashes的容量足够大,否则抛出异常
if (index >= mHashes.length) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Array is full");
}
//当数据需要插入到数组的中间,则调用put来完成
if (index > 0 && mHashes[index - 1] > hash) {
RuntimeException e = new RuntimeException("here");
e.fillInStackTrace();
Log.w(TAG, "New hash " + hash
+ " is before end of array hash " + mHashes[index - 1]
+ " at index " + index + (DEBUG ? " key " + key : ""), e);
put(key, value);
return;
}
//否则,数据直接添加到队尾
mSize = index + 1;
mHashes[index] = hash;
index <<= 1;
mArray[index] = key;
mArray[index + 1] = value;
}
append()过程跟put()很相似,append的差异在于该方法不会去做扩容的操作,是一个轻量级的插入方法。 那么什么场景适合使用append()方法呢?答应就是对于明确知道肯定会插入队尾的情况下使用append()性能更好,因为put()上来先做binarySearchHashes()二分查找,时间复杂度为O(logN),而append()的时间复杂度为O(1)。
取元素
这里的逻辑很简单,不做赘述
/**
* Retrieve a value from the array.
*
* @param key The key of the value to retrieve.
* @return Returns the value associated with the given key,
* or null if there is no such key.
*/
@Override
public V get(Object key) {
final int index = indexOfKey(key);
return index >= 0 ? (V) mArray[(index << 1) + 1] : null;
}
删除元素
删除元素为了节省内存空间可能导致缩容
/**
* Remove an existing key from the array map.
*
* @param key The key of the mapping to remove.
* @return Returns the value that was stored under the key, or null if there
* was no such key.
*/
@Override
public V remove(Object key) {
final int index = indexOfKey(key);
if (index >= 0) {
return removeAt(index);
}
return null;
}
/**
* Remove the key/value mapping at the given index.
*
* <p>For indices outside of the range <code>0...size()-1</code>, the behavior is undefined for
* apps targeting {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#P} and earlier, and an
* {@link ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException} is thrown for apps targeting
* {@link android.os.Build.VERSION_CODES#Q} and later.</p>
*
* @param index The desired index, must be between 0 and {@link #size()}-1.
* @return Returns the value that was stored at this index.
*/
public V removeAt(int index) {
if (index >= mSize && UtilConfig.sThrowExceptionForUpperArrayOutOfBounds) {
// The array might be slightly bigger than mSize, in which case, indexing won't fail.
// Check if exception should be thrown outside of the critical path.
throw new ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException(index);
}
final Object old = mArray[(index << 1) + 1];
final int osize = mSize;
final int nsize;
if (osize <= 1) { //当被移除的是ArrayMap的最后一个元素,则释放该内存
// Now empty.
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: shrink from " + mHashes.length + " to 0");
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
mHashes = EmptyArray.INT;
mArray = EmptyArray.OBJECT;
freeArrays(ohashes, oarray, osize);
nsize = 0;
} else {
nsize = osize - 1;
//根据情况来收紧容量,见上面缩容相关的分析
if (mHashes.length > (BASE_SIZE * 2) && mSize < mHashes.length / 3) {
// Shrunk enough to reduce size of arrays. We don't allow it to
// shrink smaller than (BASE_SIZE*2) to avoid flapping between
// that and BASE_SIZE.
final int n = osize > (BASE_SIZE * 2) ? (osize + (osize >> 1)) : (BASE_SIZE * 2);
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: shrink from " + mHashes.length + " to " + n);
final int[] ohashes = mHashes;
final Object[] oarray = mArray;
allocArrays(n);
//禁止并发
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS && osize != mSize) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
if (index > 0) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: copy from 0-" + index + " to 0");
System.arraycopy(ohashes, 0, mHashes, 0, index);
System.arraycopy(oarray, 0, mArray, 0, index << 1);
}
if (index < nsize) {
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: copy from " + (index + 1) + "-" + nsize
+ " to " + index);
System.arraycopy(ohashes, index + 1, mHashes, index, nsize - index);
System.arraycopy(oarray, (index + 1) << 1, mArray, index << 1,
(nsize - index) << 1);
}
} else {
if (index < nsize) {//当被移除的元素不是数组最末尾的元素时,则需要将后面的数组往前移动
if (DEBUG) Log.d(TAG, "remove: move " + (index + 1) + "-" + nsize
+ " to " + index);
System.arraycopy(mHashes, index + 1, mHashes, index, nsize - index);
System.arraycopy(mArray, (index + 1) << 1, mArray, index << 1,
(nsize - index) << 1);
}
//再将最后一个位置设置为null
mArray[nsize << 1] = null;
mArray[(nsize << 1) + 1] = null;
}
}
if (CONCURRENT_MODIFICATION_EXCEPTIONS && osize != mSize) {
throw new ConcurrentModificationException();
}
mSize = nsize; //大小减1
return (V) old;
}
使用
因为是都是使用了二分查找,所以当数据量很大时查找效率较低
假设数据量都在千级以内的情况下:
1、如果 key 的类型已经确定为 int 类型,那么使用 SparseArray,因为它避免了自动装箱的过程,如果 key 为 long 类型,它还提供了一个 LongSparseArray 来确保 key 为 long 类型时的使用
如果value确定为下面三种基本数据类型之一,那么可以采用以下三种集合来避免value的自动装箱
SparseLongArray:key为int,value为longSparseBooleanArray:key为int,value为booleanSparseIntArray:key为int,value为int
2、如果 key 类型为其它的类型,则使用 ArrayMap。
标题:spraseArray&ArrayMap源码分析
作者:OkAndGreat
地址:http://zhongtai521.wang/articles/2022/10/17/1665997666426.html